
-
Posted By Gautam Banthia
-
-
Comments 0
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
As a non-resident Indian (NRI), it’s essential to understand the rights, obligations, and benefits related to income tax. NRIs have specific tax implications based on their residential status, income sources, and country. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of income tax for NRIs, on their rights, obligations, and available deductions.
Understanding Non-Resident Indians (NRIs)
NRIs are individuals of Indian origin or descent who reside outside India for various reasons such as employment, business, education, or personal purposes. They maintain strong connections with India, including financial investments and familial ties. Understanding the NRI status is crucial for determining their tax liabilities.
How do I determine my residential status in India?
- Residential Stay Duration: The first and foremost factor is the duration of your stay in India during a financial year (1 April to 31 March). It is categorized into three types of residential statuses:
- Resident
- Non-Resident
- Not Ordinarily Resident
- Physical Presence: Apart from the duration of your stay, your physical presence in India during the financial year is also considered. The number of days you spend in India is a vital aspect of determining your residential status.
Categorization of Residential Status
Resident
If you meet either of the following conditions, you will be categorized as a resident for tax purposes:
- Stay Duration: You have been present in India for a total of 182 days or more during the financial year, or
- Stay Duration in the Past: Your cumulative stay in India for the preceding four financial years adds up to 365 days or more, and you have been in India for at least 60 days in the current financial year.
Non-Resident
If you fail to meet both conditions mentioned above, you will be considered a non-resident for tax purposes. Non-residents have different tax obligations and benefits compared to residents.
Not Ordinarily Resident
“Not Ordinarily Resident” was introduced to address individuals who have shifted their base to a foreign country. The following conditions must be met to qualify as a Not Ordinarily Resident:
- Stay Duration in India: You have been a non-resident in India for nine out of the ten previous financial years, or
- Stay Duration in India in the Past Seven Years: You have been present in India for a total of 729 days or less during the past seven financial years.
The following incomes are subject to the NRI :
Earnings from services rendered in India (worldwide income)
Gains from the sale of Indian-based assets that generated capital gains
Rental revenue from Indian-owned property
Fixed Deposits’ earnings
Bank Savings Account Interest
Consider making a fixed deposit.
Income tax slabs for NRI
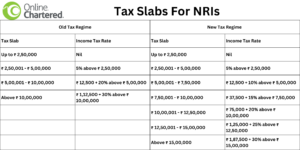
When is the last date to file an income tax return in India?
July 31st is the last date to file income tax returns in India for NRIs unless the government extends it.
Deductions available for non-resident Indians:
1. Deduction on Income from House Property
Under the Income Tax Act, NRIs can claim deductions on income generated from house property. If an NRI owns a property in India and earns rental income from it, they can deduct various expenses such as property taxes, repair costs, and home loan interest. This deduction helps reduce the taxable income derived from the property and minimizes the tax liability for NRIs.
2. Deduction on Education Loan
NRIs pursuing higher education or supporting their children’s education in India can avail of a deduction on the interest paid on education loans. This deduction is available under Section 80E of the Income Tax Act and applies to loans taken for higher studies, including graduate and post-graduate courses. NRIs can claim this deduction for a maximum of eight consecutive years or until the interest is fully repaid, whichever is earlier.
3. Deduction on Health Insurance Premium
Healthcare costs can be significant, and NRIs can benefit from deductions on health insurance premiums. Under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act, NRIs can claim deductions for health insurance premiums paid for themselves, their spouse, children, and parents. The deduction limits vary based on the age of the individual and their family members, providing NRIs with an opportunity to reduce their tax liability while ensuring adequate health coverage.
4. Deduction on Donations to Charitable Organizations
The Indian tax system recognizes their contributions through deductions on donations made to charitable organizations. NRIs can claim deductions under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act for grants to eligible charitable institutions. It is crucial to ensure that the organization is registered and qualifies for tax deductions before making any contributions.
Conclusion
Understanding income tax for NRIs is crucial for ensuring compliance and optimizing tax liabilities. NRIs have specific rights, obligations, and benefits under the Income Tax Act. By familiarizing themselves with the residential status rules, available deductions, and tax planning strategies, NRIs can effectively manage their tax affairs and make informed financial decisions.
FAQs
1. Do NRIs have to pay tax on their global income in India?
No, NRIs are generally taxed only on income earned or accrued in India. Income earned abroad by NRIs is usually not taxable in India.
2. Can NRIs claim tax benefits and deductions available to resident Indians?
NRIs can claim tax benefits and deductions available under the Income Tax Act, provided they meet the specified criteria.
3. Are NRIs eligible for the same tax exemptions as resident Indians?
Yes, NRIs can avail themselves of the same tax exemptions as resident Indians, subject to meeting the prescribed conditions.
4. What is the importance of Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA) for NRIs?
DTAA provides relief to NRIs by preventing double taxation on the same income. It ensures a fair allocation of tax liabilities between India and the country of residence.
5. Can NRIs file income tax returns electronically?
Yes, NRIs can file income tax returns electronically using the e-filing portal provided by the Indian government.
You might be interested In this:




