File Income Tax Return (ITR) Online
File your Income tax return online with our expert
What do we mean by Income Tax Return (ITR) Online
Income Tax Return is the form in which assessee files information about his Income and tax thereon to Income Tax Department. The Income Tax Act, 1961, and the Income Tax Rules, 1962, obligates citizens to file returns with the Income Tax Department at the end of every financial year. These returns should be filed before the specified due date. Every Income Tax Return Form is applicable to a certain section of the Assessees.
ITR FORMS
| ITR FORM | APPLICABLE TO.. | NOT APPLICABLE TO.. |
| ITR-1 OR SAHAJ | This Return Form is applicable to a resident individual whose total income for the assessment year 2020-21 includes: -Income from Salary/ Pension; or -Income from One House Property (excluding cases where loss is brought forward from previous years); or -Income from Other Sources (excluding Winning from Lottery and Income from Race Horses) -Agricultural income up to Rs.5000. | -In case the total income that has been generated is more than Rs.50,000. -In case individuals have capital gains that are taxable. -In case income is generated from more than one house property. During the financial year, if any investments were present in unlisted equity shares. -In case you are a Non-Resident Indian (NRI) and Resident Not Ordinary Resident (RNOR). -In case income that is generated from agriculture is more than Rs.5,000. -In case income is generated from profession or business. -In case the individual is the director of a company. -In case any income is generated from a property that is located outside India. -In case an individual has foreign assets or foreign income |
| ITR-2 | This form is appliable to individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) who fall under the below-mentioned categories: Income of the individual must be more than Rs.50 lakh. Income can be generated via a pension or from salary. Income that is generated from house property. Income that is generated from winning a lottery or horse races. In case the individual is the Director of a company. Agricultural income of the individual is more than Rs.5,000. Income has been generated from capital gains. In case any investments were present in equity shares that were unlisted during the financial year. Income is generated from foreign income and foreign assets. | Individuals who make an income from profession and business can opt for the form. |
| ITR-3 | This form is applicable to an individual or a Hindu Undivided Family who have income from proprietary business or are carrying on profession. The persons having income from following sources are eligible to file ITR 3: Individuals who are generating an income from a profession or business. In case any investments were present in equity shares that were unlisted at any time during the financial year. In case the individual is a partner in a firm. In case the individual is a Director of a company. If income is generated from a pension or salary, house property, or any other source of income. Turnover of the business exceeds Rs.2 crore | This form is not applicable to those who are specifically falling in to any other catagory of the other forms of ITRS. |
| ITR-4 OR SUGAM | This form is applicable to individuals and HUFs, Partnership firms (other than LLPs) which are residents having income from a business or profession. Its applicable to those who have opted for the presumptive income scheme as per Section 44AD, Section 44ADA and Section 44AE of the Income Tax Act. However, if the turnover of the business exceeds Rs 2 crore, the taxpayer will have to file ITR-3. | If your total income exceeds Rs 50 lakh Having income from more than one house property If you have any brought forward loss or loss to be carried forward under any head of income Owning any foreign asset If you have signing authority in any account located outside India Having income from any source outside India If you are a Director in a company If you have had investments in unlisted equity shares at any time during the financial year Being a resident not ordinarily resident (RNOR) and non-resident Having foreign assets or foreign income If you are assessable in respect of income of another person in respect of which tax is deducted in the hands of the other person. |
| ITR-5 | This form is applicable to Investment funds, Business trusts, Estate of insolvent, Estate of deceased, Artificial Juridical Person (AJP), Body of Individuals (BOIs), Associations of Persons (AOPs), LLPs, and firms. | |
| ITR-6 | This form is applicable to any companies that are not claiming exemptions under Section 11. Any Company that is filing returns under this section can only do it electronically. | |
| ITR-7 | This form is applicable to Individuals and companies that have furnished returns under Section 139(4A), Section 139(4B), Section 139(4C), Section 139(4D), Section 139(4E), or Section 139(4F). Now, Let us see what these sections are all about: Section 139(4A): The returns must be filed by individuals who receive an income from a property that belongs to a trust or other legal obligations and the income that is generated is solely used for religious or charitable purposes. Section 139(4B): Returns must be filed under this section by a political party if the total income that has been generated is more than the maximum amount. Section 139(4C): Returns must be filed under this section by the below-mentioned entities: – Scientific Research association – Institutions or association that come under Section 10(23A) – Medical institutions, hospitals, universities, funds, and other educational institutions. – News agencies – Institutions that come under Section 10(23B) Section 139(4D): Any college, university, or other institutions that are not required to furnish any income or loss must file returns under this section. Section 139(4E): Business trusts that are not required to furnish their income or loss must file their returns under this section. Section 139(4F): Investment funds that are present under Section 115UB and are not required to furnish any income or losses must file returns under this section. |
Why you should file your Income tax returns?
1) TO SAVE YOURSELF FROM PENALTY: The Income Tax Department levies a penalty of Rs 10,000 under section 234F on individuals who do not file their income tax return. Filing ITR on time avoids unnecessary penalties. Even though the penalty has been kept at Rs 1,000 if your annual income is not more than Rs 5 lakh, as a law-abiding citizen, it is your duty to file your tax returns.
2) TO GET LOAN OR CREDIT CARD: If you plan to apply for a home loan in future it is a good idea to maintain a steady record of filing returns as the home loan company will most likely insist on it. In fact, you may even consider filing your spouse’s returns if you want to apply for a loan as a co-borrower. Likewise, even credit card companies may insist on proof of return before issuing a card. Financial institutions may insist on seeing your returns over the past few years before transacting with you. In fact, the government may make it mandatory for them to do so, thereby indirectly nudging individuals to file returns regularly even when it’s voluntary.
3) TO GET VISA: Embassies of developed countries like the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia ask for ITR receipts of the past years to process your visa application. They are very particular about your tax compliance and hence, you are asked to furnish past ITR receipts. This helps them assess your income and ensure that you are able to take care of the expenses on your trip.
4) TO CLAIM REFUND: There could be a possibility that there has been tax deducted at source (TDS) on some investment made in the name of the individual. If TDS has been cut, one will have to file the ITR to claim refund of the same.
5) TO CARRY FORWARD LOSS: Income tax rules allow carry-forward losses to set them off against capital gains only to those who file ITR in the relevant assessment year. There are certain instances that you may have incurred losses for a year. In such a scenario, you cannot stay away from filing of your return saying you have an income below the exemption limit. In fact, you must ideally file your return so that you can carry forward the losses you have incurred to set it off against the income of the subsequent years.
Original due dates for Income Tax Return Filing
FOR INDIVIDUAL: 31ST JULY OF SUBSEQUENT YEAR
BODY OF INDIVIDUALS: 31ST JULY OF SUBSEQUENT YEAR
HINDU UNDIVIDED FAMILY: 31ST JULY OF SUBSEQUENT YEAR
ASSOCIATION OF PERSON: 31ST JULY OF SUBSEQUENT YEAR
BUSINESS (AUDITED CASES): 30TH SEPETEMBER OF SUBSEQUENT YEAR
BUSINESS (REQUIRING TP REPORT): 30TH NOVEMBER OF SUBSEQUENT YEAR
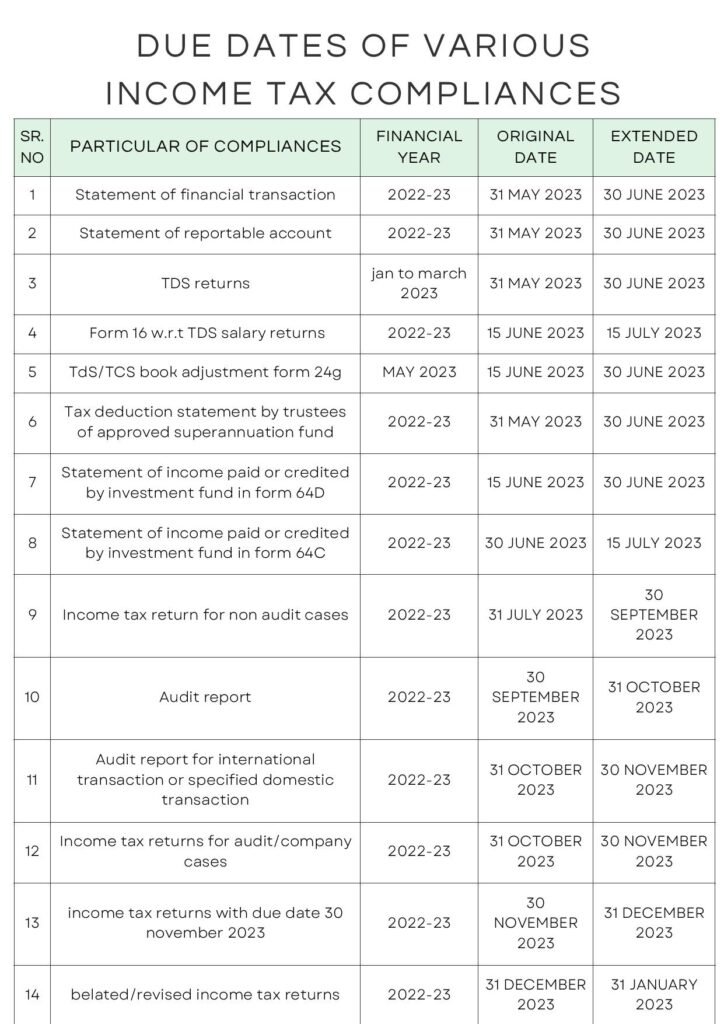
Extended due dates of various Income tax compliances

Ask an expert
Get answers to all your queries
ITR can be filed at www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in.
Every Indian citizen whose gross total income exceeds the taxable limit must file an ITR. This means that, individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) with total annual income exceeding Rs 250,000 lakh are required to file income tax returns. For senior citizens (individuals between 60 years and 80 years of age) the threshold is Rs 300,000, and that for very senior citizens (aged above 80 years) it is Rs 500,000.
YES, ITR can be revised within prescribed time limit.
The password to open ITR-V is the combination of your PAN number and your DOB. It should be last 5 digits of your PAN number and ddmmyyyy of the DOB.
All the CPC communications are done by email and mobile number and that is why you must check this information first. Go to the E-filing website and access the user account and review the details. For help, contact your tax practitioner.
It is 8.00 am to 8.00 pm from Monday to Friday, excluding all the national holidays.
The excess tax can be claimed as refund by filing your income tax return (ITR). After your return is processed and provided the tax department accepts your refund claim, the amount claimed as refund would l be credited back to your bank account through Electronic Clearance Service (ECS) transfer.
No, it is not mandatory to file an income tax return if your annual income is below Rs 250,000. However, even those who are out of the tax net should consider filing a 'Nil Return' to maintain a record. There are several instances where income tax returns are considered a proof of employment — for instance, when you are applying for a passport or taking a loan. it is always advisable to file ITR even if your income is below basic exemption limit. This helps you in many ways.
ITR-V is the acknowledgement of ITR.
You can do it multiple times till the expiry of one year time limit.
Toll free number of CPC is 1800-425-2229. You can use the chargeable number 080-22546500 to contact IT department.
